配置Rsyslog使用TCP/TLS协议加密传输日志
测试环境
操作系统:CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)
Rsyslog Server: 10.10.0.102
Rsyslog Client: 10.10.0.100
CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)默认安装rsyslog版本为8.24.0-55.el7
安装rsyslog-gnutls组件会升级rsyslog的版本。
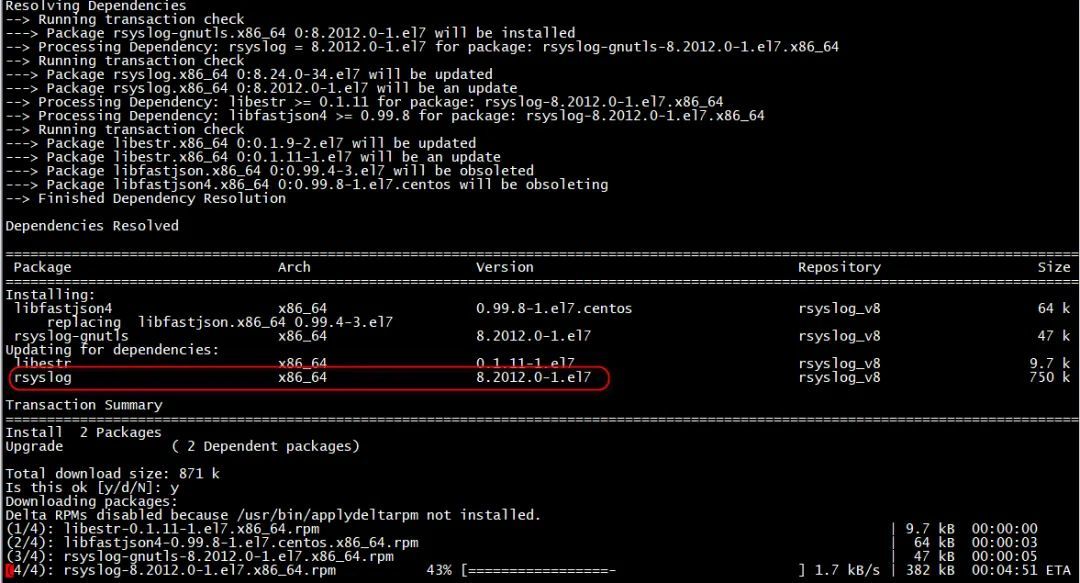
1 安装rsyslog-gnutls组件
1.1 配置rsyslog-gnutls组件yum源
会升级rsyslog的版本,请注意!
]$ cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
]$ wget http://rpms.adiscon.com/v8-stable/rsyslog.repo
]$ yum install rsyslog-gnutls
2 创建自签证书
certtool命令非系统自带命令,需要进行安装。]$ yum install -y gnutls-utils
2.1 创建自签CA证书
2.1.1 创建CA私钥
]$ certtool --generate-privkey --outfile ca-key.pem
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key...
2.1.2 创建CA证书
]$ certtool --generate-self-signed --load-privkey ca-key.pem --outfile ca.pem
Generating a self signed certificate...
Please enter the details of the certificate's distinguished name. Just press enter to ignore a field.
Common name: rsyslog-server
UID:
Organizational unit name: eccom
Organization name: eccom
Locality name: gd
State or province name: gd
Country name (2 chars): cn
Enter the subject's domain component (DC):
This field should not be used in new certificates.
E-mail:
Enter the certificate's serial number in decimal (default: 7205860249691488368):
Activation/Expiration time.
The certificate will expire in (days): 3650
Extensions.
Does the certificate belong to an authority? (y/N):
Path length constraint (decimal, -1 for no constraint):
Is this a TLS web client certificate? (y/N):
Enter a dnsName of the subject of the certificate:
Enter a URI of the subject of the certificate:
Enter the IP address of the subject of the certificate:
Enter the e-mail of the subject of the certificate:
Will the certificate be used to sign OCSP requests? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used to sign code? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used for time stamping? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used to sign other certificates? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used to sign CRLs? (y/N):
Enter the URI of the CRL distribution point:
X.509 Certificate Information:
Version: 3
Serial Number (hex): 64005bb803f80070
Validity:
Not Before: Thu Mar 02 08:18:01 UTC 2023
Not After: Sun Feb 27 08:18:20 UTC 2033
Subject: CN=rsyslog-server,OU=eccom,O=eccom,L=gd,ST=gd,C=cn
Subject Public Key Algorithm: RSA
Algorithm Security Level: Medium (2048 bits)
Modulus (bits 2048):
00:d2:95:e7:64:20:cd:2e:a8:69:fd:3f:ed:6e:80:51
1f:79:c8:00:86:de:e0:e6:80:d1:e7:86:02:be:56:1c
de:9d:ca:ec:78:d0:aa:a1:99:4e:f4:db:d4:73:7f:3b
e4:54:46:0f:f2:f5:7f:0f:cf:95:d7:83:d4:a8:b5:2a
96:e9:41:45:c9:61:33:50:35:a4:5e:12:79:69:53:15
15:aa:f5:12:b0:cc:8e:48:79:74:bf:e2:f7:ff:29:c0
f9:84:64:1f:41:17:c8:63:cc:a2:79:2e:d7:d3:16:36
48:36:d5:0b:e0:b3:e1:60:a7:2b:c3:54:90:29:9b:73
d9:36:4e:a5:9b:96:93:7c:b9:bc:b3:97:01:57:34:ab
82:dc:46:0c:01:38:1b:cb:e3:18:89:ee:33:33:5d:23
b9:41:4a:a8:7f:f8:a4:84:b1:0b:57:1b:13:2c:ae:09
50:b8:a6:15:6d:79:62:32:b2:48:e6:5b:fc:95:37:73
96:0e:5e:a3:c1:67:bd:e4:b0:4b:91:67:b1:7b:0e:b1
2b:68:27:a9:12:dc:2b:18:d9:3b:5d:d8:bc:d1:8b:9c
ef:00:63:a1:b6:55:07:5e:ff:30:e0:10:6c:7b:b8:5b
53:14:3c:8c:c7:4b:1a:47:94:3b:b6:e1:6c:16:3d:6d
47
Exponent (bits 24):
01:00:01
Extensions:
Basic Constraints (critical):
Certificate Authority (CA): TRUE
Subject Key Identifier (not critical):
db8277d26bc2ab483d2f663142eddf212b43977f
Other Information:
Public Key ID:
db8277d26bc2ab483d2f663142eddf212b43977f
Public key's random art:
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
| |
| |
| . |
| . . |
| . . S. |
| ..=.++. |
| .o+*==+. |
| . .*+=++.E |
| .o.=o+.. |
+-----------------+
Is the above information ok? (y/N): y
Signing certificate...
]$ ll
total 12
-rw-------. 1 root root 5816 Mar 2 03:13 ca-key.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1285 Mar 2 03:19 ca.pem
2.2 创建客户端证书
在rsyslog server服务器上进行创建,创建完成后,复制到rsyslog client服务器
2.2.1 创建单独客户端私钥
]$ certtool --generate-privkey --outfile key.pem
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key...
2.2.2 生成单独客户端请求证书
不要将其与CA的私钥混淆 - 这个是不同的
]$ certtool --generate-request --load-privkey key.pem --outfile request.pem
Generating a PKCS #10 certificate request...
Common name: rsyslog-client
Organizational unit name: eccom
Organization name: eccom
Locality name: gd
State or province name: gd
Country name (2 chars): cn
Enter the subject's domain component (DC):
UID:
Enter a dnsName of the subject of the certificate:
Enter a URI of the subject of the certificate:
Enter the IP address of the subject of the certificate:
Enter the e-mail of the subject of the certificate:
Enter a challenge password:
Does the certificate belong to an authority? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used for signing (DHE and RSA-EXPORT ciphersuites)? (Y/n):
Will the certificate be used for encryption (RSA ciphersuites)? (Y/n):
Will the certificate be used to sign code? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used for time stamping? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used for IPsec IKE operations? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used to sign OCSP requests? (y/N):
Is this a TLS web client certificate? (y/N):
Is this a TLS web server certificate? (y/N):
] $ ll
total 12
-rw-------. 1 root root 5816 Mar 2 03:13 ca-key.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1285 Mar 2 03:19 ca.pem
-rw-------. 1 root root 5816 Mar 2 03:21 key.pem
-rw-------. 1 root root 2428 Mar 2 03:27 request.pem
2.2.3 对请求证书进行签名(验证、授权)并生成客户端证书
]$ certtool --generate-certificate --load-request request.pem --outfile cert.pem --load-ca-certificate ca.pem --load-ca-privkey ca-key.pem
Generating a signed certificate...
Enter the certificate's serial number in decimal (default: 7205865592876789725):
Activation/Expiration time.
The certificate will expire in (days): 1800
Extensions.
Do you want to honour the extensions from the request? (y/N):
Does the certificate belong to an authority? (y/N):
Path length constraint (decimal, -1 for no constraint):
Is this a TLS web client certificate? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used for IPsec IKE operations? (y/N):
Is this a TLS web server certificate? (y/N):
Enter a dnsName of the subject of the certificate:
Enter a URI of the subject of the certificate:
Enter the IP address of the subject of the certificate:
Enter the e-mail of the subject of the certificate:
Will the certificate be used to sign OCSP requests? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used to sign code? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used for time stamping? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used to sign other certificates? (y/N):
Will the certificate be used to sign CRLs? (y/N):
X.509 Certificate Information:
Version: 3
Serial Number (hex): 6400609412a16fdd
Validity:
Not Before: Thu Mar 02 08:38:45 UTC 2023
Not After: Fri Feb 04 08:38:50 UTC 2028
Subject: CN=rsyslog-client,OU=eccom,O=eccom,L=gd,ST=gd,C=cn
Subject Public Key Algorithm: RSA
Algorithm Security Level: Medium (2048 bits)
Modulus (bits 2048):
00:ac:8b:79:80:54:3d:a4:9c:f0:9a:63:2d:4d:75:ae
f1:b9:98:ce:fa:d2:ba:d3:63:55:3b:fc:79:53:2c:e3
29:ba:cd:19:65:74:b0:f2:58:ee:8f:19:b3:ac:21:6b
d7:fa:29:f9:90:ec:04:6c:17:cc:f8:5e:78:2d:7f:62
bb:97:70:f4:6b:7a:2f:dc:c6:b7:08:48:8e:8d:2f:db
32:46:7a:3e:e2:79:1c:27:8b:f7:31:0b:d8:52:79:66
b7:6d:d7:59:ca:d3:9c:80:7a:42:de:14:44:19:ef:be
f6:f0:d8:e1:e9:39:24:3d:3e:e6:05:26:ac:d2:9e:3a
47:e7:75:b0:5b:33:8e:01:0a:d7:36:05:c8:4d:27:2f
b5:55:1a:f2:b7:80:42:b5:be:90:b4:98:74:c5:a7:3c
1c:67:cb:59:89:f0:90:15:9d:54:e9:bb:47:e0:71:b4
b9:ae:7f:21:c4:2c:f4:74:27:32:cd:cf:1e:80:13:3e
a3:37:c1:df:20:b6:d8:e4:81:e7:b4:5a:eb:29:40:3b
86:82:d1:ed:16:23:2b:a5:fe:62:e3:79:3d:91:16:80
83:67:6a:ec:d3:3e:c7:20:f6:9b:f6:96:a4:02:6f:c6
12:2c:ad:05:1a:94:44:4e:5b:9d:97:95:fc:9f:1a:3a
2d
Exponent (bits 24):
01:00:01
Extensions:
Basic Constraints (critical):
Certificate Authority (CA): TRUE
Key Usage (critical):
Digital signature.
Key encipherment.
Subject Key Identifier (not critical):
a058f56a51fde803887322e3ac39d6341b468911
Authority Key Identifier (not critical):
db8277d26bc2ab483d2f663142eddf212b43977f
Other Information:
Public Key ID:
a058f56a51fde803887322e3ac39d6341b468911
Public key's random art:
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
| E. . .. |
| . . o . |
| o o.o.. o |
| .o=+.o+. . . |
| ooo.+o So |
| o= . o |
| o+ + . |
|+. o |
|.. |
+-----------------+
Is the above information ok? (y/N): y
Signing certificate...
[root@splunk-sh02 ssl]# ll
total 28
-rw-------. 1 root root 5816 Mar 2 03:13 ca-key.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1285 Mar 2 03:19 ca.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1342 Mar 2 03:41 cert.pem
-rw-------. 1 root root 5816 Mar 2 03:21 key.pem
-rw-------. 1 root root 2428 Mar 2 03:27 request.pem
2.2.4 证书校验
]$ certtool --certificate-info --infile cert.pem
3 证书分发
# 删除request.pem证书
] $ rm -rf request.pem
# 将key.pem和cert.pem重命名
] $ mv cert.pem machine-cert.pem
] $ mv key.pem machine-key.pem
] $ ll
total 24
-rw-------. 1 root root 5823 Feb 25 18:06 ca-key.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1281 Feb 25 18:08 ca.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1322 Feb 25 18:09 machine-cert.pem
-rw-------. 1 root root 5813 Feb 25 18:08 machine-key.pem
# 将ca.pem证书复制到rsyslog client服务器上/etc/rsyslog.d/目录中
]$ scp ca.pem root@10.10.0.100:/etc/rsyslog.d
4 Rsyslog Server配置文件
# rsyslog configuration file
# For more information see /usr/share/doc/rsyslog-*/rsyslog_conf.html
# If you experience problems, see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/troubleshoot.html
#### MODULES ####
# The imjournal module bellow is now used as a message source instead of imuxsock.
$ModLoad imuxsock
# provides support for local system logging (e.g. via logger command)
$ModLoad imjournal
# provides access to the systemd journal
#$ModLoad imklog # reads kernel messages (the same are read from journald)
#$ModLoad immark # provides --MARK-- message capability
# Provides UDP syslog reception
#$ModLoad imudp
#$UDPServerRun 514
# Provides TCP syslog reception
#$ModLoad imtcp
#$InputTCPServerRun 514
#### GLOBAL DIRECTIVES ####
# Where to place auxiliary files
$WorkDirectory /var/lib/rsyslog
# Use default timestamp format
$ActionFileDefaultTemplate RSYSLOG_TraditionalFileFormat
# File syncing capability is disabled by default. This feature is usually not required,
# not useful and an extreme performance hit
#$ActionFileEnableSync on
# Include all config files in /etc/rsyslog.d/
$IncludeConfig /etc/rsyslog.d/*.conf
# Turn off message reception via local log socket;
# local messages are retrieved through imjournal now.
$OmitLocalLogging on
# File to store the position in the journal
$IMJournalStateFile imjournal.state
#### RULES ####
# Log all kernel messages to the console.
# Logging much else clutters up the screen.
#kern.* /dev/console
# Log anything (except mail) of level info or higher.
# Don't log private authentication messages!
# *.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none /var/log/messages
# 上述配置内容可以注释掉,当rsyslog client发送日志到rsyslog Server同时会保存在template和/var/log/messages
# The authpriv file has restricted access.
authpriv.* /var/log/secure
# Log all the mail messages in one place.
mail.* -/var/log/maillog
# Log cron stuff
cron.* /var/log/cron
# Everybody gets emergency messages
*.emerg :omusrmsg:*
# Save news errors of level crit and higher in a special file.
uucp,news.crit /var/log/spooler
# Save boot messages also to boot.log
local7.* /var/log/boot.log
# ### begin forwarding rule ###
# The statement between the begin ... end define a SINGLE forwarding
# rule. They belong together, do NOT split them. If you create multiple
# forwarding rules, duplicate the whole block!
# Remote Logging (we use TCP for reliable delivery)
#
# An on-disk queue is created for this action. If the remote host is
# down, messages are spooled to disk and sent when it is up again.
#$ActionQueueFileName fwdRule1 # unique name prefix for spool files
#$ActionQueueMaxDiskSpace 1g # 1gb space limit (use as much as possible)
#$ActionQueueSaveOnShutdown on # save messages to disk on shutdown
#$ActionQueueType LinkedList # run asynchronously
#$ActionResumeRetryCount -1 # infinite retries if host is down
# remote host is: name/ip:port, e.g. 192.168.0.1:514, port optional
#*.* @@remote-host:514
#####################################################################################################################################
###########################################################华丽的分割线################################################################
#####################################################tcp/tsl加密添加以下内容###########################################################
$ModLoad imuxsock # local messages
$ModLoad imtcp # TCP listener
# make gtls driver the default
# 默认为GTLS驱动程序
$DefaultNetstreamDriver gtls
# certificate files
# CA 密钥
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCAFile /etc/rsyslog.d/ca.pem
# 客户端证书
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCertFile /etc/rsyslog.d/machine-cert.pem
# 客户端私钥
$DefaultNetstreamDriverKeyFile /etc/rsyslog.d/machine-key.pem
# 驱动程序认证模式
$InputTCPServerStreamDriverAuthMode anon
# 在tls模式下运行驱动程序
$InputTCPServerStreamDriverMode 1
# 在1514端口启动监听器,接收发送到tcp/1514端口上的数据
$InputTCPServerRun 1514
## 数据保存策略
$template Remote,"/var/log/syslog/%fromhost-ip%/%$YEAR%-%$MONTH%-%$DAY%.log"
:fromhost-ip, !isequal, "127.0.0.1" ?Remote
& ~
# 注意此规则需要在其它规则之前,否则配置没有意义,远程主机的日志也会记录到Server的日志文件中
# 忽略之前所有的日志,远程主机日志记录完之后不再继续往下记录
# ### end of the forwarding rule ###
4.1 坑
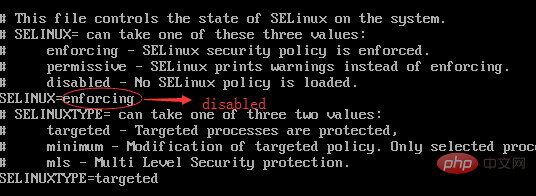
将rsyslog tcp 数据接收端口设置为1514时候,重启rsyslog报tcp socket: Permission denied权限问题,需要关闭selinux。
Feb 25 17:50:32 linux-syslogserver rsyslogd[2042]: Error while binding tcp socket: Permission denied [v8.2302.0]
Feb 25 17:50:32 linux-syslogserver rsyslogd[2042]: Error while binding tcp socket: Permission denied [v8.2302.0]
临时关闭:setenforce 0
永久关闭,需要重启:
] $ vi /etc/selinux/config
] $ cat /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
# SELINUX=enforcing
# 设置为disabled
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
5 Rsyslog Client配置文件
# rsyslog configuration file
# For more information see /usr/share/doc/rsyslog-*/rsyslog_conf.html
# If you experience problems, see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/troubleshoot.html
#### MODULES ####
# The imjournal module bellow is now used as a message source instead of imuxsock.
$ModLoad imuxsock # provides support for local system logging (e.g. via logger command)
$ModLoad imjournal # provides access to the systemd journal
#$ModLoad imklog # reads kernel messages (the same are read from journald)
#$ModLoad immark # provides --MARK-- message capability
# Provides UDP syslog reception
#$ModLoad imudp
#$UDPServerRun 514
# Provides TCP syslog reception
#$ModLoad imtcp
#$InputTCPServerRun 514
#### GLOBAL DIRECTIVES ####
# Where to place auxiliary files
$WorkDirectory /var/lib/rsyslog
# Use default timestamp format
$ActionFileDefaultTemplate RSYSLOG_TraditionalFileFormat
# File syncing capability is disabled by default. This feature is usually not required,
# not useful and an extreme performance hit
#$ActionFileEnableSync on
# Include all config files in /etc/rsyslog.d/
$IncludeConfig /etc/rsyslog.d/*.conf
# Turn off message reception via local log socket;
# local messages are retrieved through imjournal now.
$OmitLocalLogging on
# File to store the position in the journal
$IMJournalStateFile imjournal.state
#### RULES ####
# Log all kernel messages to the console.
# Logging much else clutters up the screen.
#kern.* /dev/console
# Log anything (except mail) of level info or higher.
# Don't log private authentication messages!
*.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none /var/log/messages
# The authpriv file has restricted access.
authpriv.* /var/log/secure
# Log all the mail messages in one place.
mail.* -/var/log/maillog
# Log cron stuff
cron.* /var/log/cron
# Everybody gets emergency messages
*.emerg :omusrmsg:*
# Save news errors of level crit and higher in a special file.
uucp,news.crit /var/log/spooler
# Save boot messages also to boot.log
local7.* /var/log/boot.log
# ### begin forwarding rule ###
# The statement between the begin ... end define a SINGLE forwarding
# rule. They belong together, do NOT split them. If you create multiple
# forwarding rules, duplicate the whole block!
# Remote Logging (we use TCP for reliable delivery)
# An on-disk queue is created for this action. If the remote host is
# down, messages are spooled to disk and sent when it is up again.
#$ActionQueueFileName fwdRule1 # unique name prefix for spool files
#$ActionQueueMaxDiskSpace 1g # 1gb space limit (use as much as possible)
#$ActionQueueSaveOnShutdown on # save messages to disk on shutdown
#$ActionQueueType LinkedList # run asynchronously
#$ActionResumeRetryCount -1 # infinite retries if host is down
# remote host is: name/ip:port, e.g. 192.168.0.1:514, port optional
#*.* @@remote-host:514
#####################################################################################################################################
#######################################################华丽的分割线####################################################################
####################################################tcp/tsl加密添加以下内容############################################################
# make gtls driver the default
$DefaultNetstreamDriver gtls
# certificate files
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCAFile /etc/rsyslog.d/ca.pem
$ActionSendStreamDriverAuthMode anon
$ActionSendStreamDriverMode 1
*.* @@10.10.0.102:1514
# ### end of the forwarding rule ###
6 验证日志接收
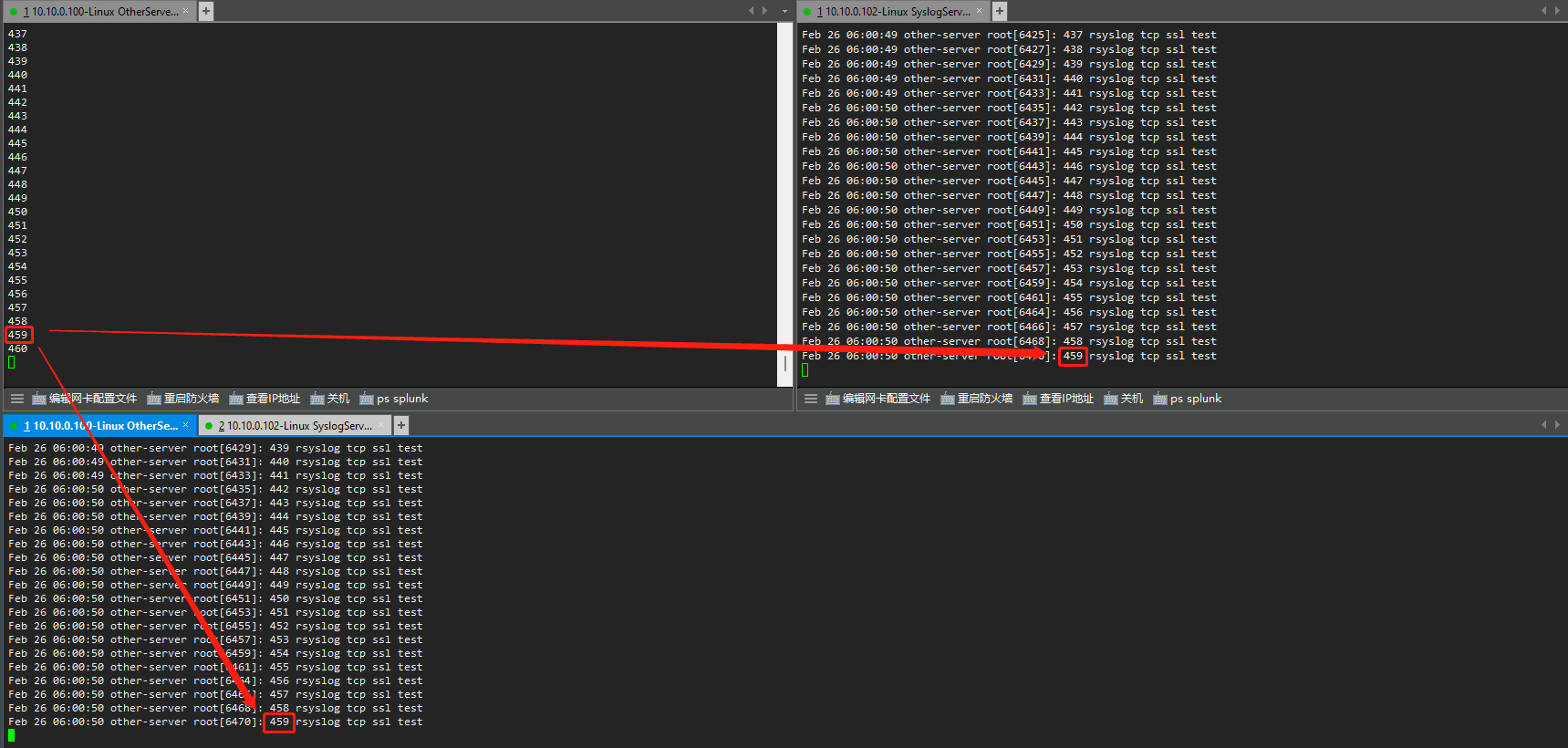
验证脚本,循环一万次产生syslog日志,转发到syslog-server。
[rsyslog@other-server pem]$ cat logger.sh #!/bin/bash number=0 while [[ $number -le 10000 ]]; do echo $number sleep 0.05 `logger "$number rsyslog tcp ssl test"` ((a++)) done
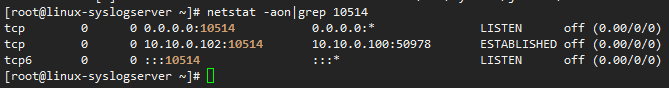
端口链接状态
使用tcpdump抓包查看:
tcpdump -i ens33 -vv tcp port 10514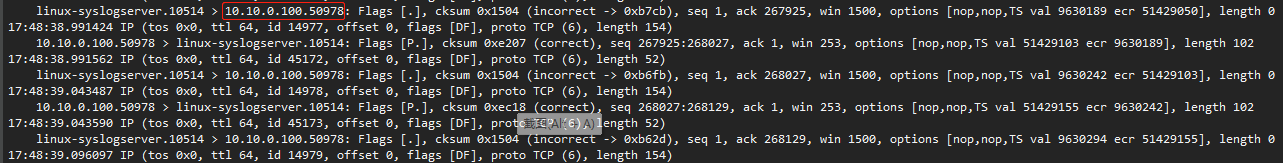
syslog 数据发送情况确认
7 使用Splunk生成的证书
7.1 使用splunk生成证书
会在当前目录下生成myKey.key和myCert.pem文件
/opt/splunk/bin/splunk cmd openssl req -x509
-newkey rsa:4096
-keyout myKey.key
-out myCert.pem
-sha256
-days 365
-batch
-nodes
-subj “/C=CN/ST=guangdong/L=shenzhen/O=Eccom/OU=IT/CN=linux-syslogserver.eccom.com.cn”
[root@splunk-master ~]# /opt/splunk/bin/splunk cmd openssl req -x509 \
-newkey rsa:4096 \
-keyout myKey.key \
-out myCert.pem \
-sha256 \
-days 365 \
-batch \
-nodes \
-subj "/C=CN/ST=guangdong/L=shenzhen/O=Eccom/OU=IT/CN=linux-syslogserver.eccom.com.cn"
Generating a RSA private key
......................................................................................................................................................................++++
writing new private key to 'myKey.key'
-----
[root@linux-syslogserver tls]# ll
total 8
-rw-------. 1 root root 2220 Apr 17 08:17 myCert.pem
-rw-------. 1 root root 3272 Apr 17 08:17 myKey.key
| 参数 | 示例 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| C | CN | 国家(Country Name) |
| ST | guangdong | 州或省(State or Province Name) |
| L | shenzhen | 地区或市(Locality Name) |
| O | Eccom | 组织(Organization Name) |
| OU | IT | 部门(Organization Unit Name) |
| CN | linux-syslogserver | 证书使用者的通用名称(Common Name) |
7.2 rsyslog service配置
# TCP/SSL Test
$ModLoad imuxsock # local messages
$ModLoad imtcp # TCP listener
# make gtls driver the default
$DefaultNetstreamDriver gtls
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCAFile /opt/tls/myCert.pem
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCertFile /opt/tls/myCert.pem
$DefaultNetstreamDriverKeyFile /opt/tls/myKey.key
$InputTCPServerStreamDriverAuthMode anon
$InputTCPServerStreamDriverMode 1 # run driver in TLS-only mode
$InputTCPServerRun 1514 # start up listener at port 1514
$template Remote,"/var/log/syslog/%fromhost-ip%/%$YEAR%-%$MONTH%-%$DAY%.log"
:fromhost-ip, !isequal, "127.0.0.1" ?Remote
& ~
7.3 rsyslog client配置
$DefaultNetstreamDriver gtls
# certificate files
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCAFile /etc/rsyslog.d/myCert.pem
$ActionSendStreamDriverAuthMode anon
$ActionSendStreamDriverMode 1
*.* @@10.10.0.102:1514
参考链接:
CentOS7下使用TCP over TLS方式安全传输远程主机系统日志 - 腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云 (tencent.com)
Generating the machine certificate — rsyslog 8.18.0.master documentation
Encrypting Syslog Traffic with TLS (SSL) short version — rsyslog 8.18.0.master documentation
rsyslog如何收集远程日志但不写入本地messages? - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
[linux怎么关闭selinux-linux运维-PHP中文网](https://www.php.cn/linux-491272.html#:~:text=关闭方法:1、临时关闭,只需执行“setenforce 0”命令即可。 2、永久关闭,需要执行“vi,%2Fetc%2Fselinux%2Fconfig”命令打开config文件,将“SELINUX”项的值改为“disabled”,保存文件并退出即可。 本教程操作环境:linux5.9.8系统、Dell G3电脑。)
How to run rsyslog as a non-root user in CentOS/RHEL 7 – The Geek Diary


-d2979772834f4346a961b123d2a49447.jpg)


评论区